模型视图控制器 (MVC) 编程哪家讲的好,莫非是 Qt 帮助文档里的 Model/View Programming 了,可惜没有中文的,看过不少书里这方面的内容都是从这篇文档里抄的,我们就不要再花心思去创新了,直接翻译吧。
模型视图编程简介
Qt contains a set of item view classes that use a model/view architecture to manage the relationship between data and the way it is presented to the user. The separation of functionality introduced by this architecture gives developers greater flexibility to customize the presentation of items, and provides a standard model interface to allow a wide range of data sources to be used with existing item views. In this document, we give a brief introduction to the model/view paradigm, outline the concepts involved, and describe the architecture of the item view system. Each of the components in the architecture is explained, and examples are given that show how to use the classes provided.
Qt 中有几个 item view 的类 (视图),使用模型/视图架构来管理和显示数据。这种分离的设计给开发者很高的灵活性,可以自定义数据的显示方式,视图通过模型提供的标准接口可以支持各种各样的数据源。本文涉及到模型/视图编程范例、简要的概念介绍以及描述视图系统的架构。每一个部分都会进行解释以及给出相关代码展示怎么使用。
模型视图架构
Model-View-Controller (MVC) is a design pattern originating from Smalltalk that is often used when building user interfaces. In Design Patterns, Gamma et al. write:
MVC consists of three kinds of objects. The Model is the application object, the View is its screen presentation, and the Controller defines the way the user interface reacts to user input. Before MVC, user interface designs tended to lump these objects together. MVC decouples them to increase flexibility and reuse.
Smalltalk 经常用来构建用户界面,模型-视图-控制器 (MVC) 这种设计模式就是从 Smalltalk 借鉴而来的。Gamma et al. 在设计模式中写到:
MVC 由 3 种对象组成:Model 是应用的数据,View 显示数据,Controller 定义了用户界面对用户输入的响应。在使用 MVC 之前,用户界面的设计常常把这些对象耦合在一起。MVC 能够解耦它们从而提供更高的灵活性和重用性。
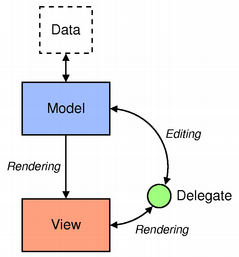
The view obtains model indexes from the model; these are references to items of data. By supplying model indexes to the model, the view can retrieve items of data from the data source.
In standard views, a delegate renders the items of data. When an item is edited, the delegate communicates with the model directly using model indexes.
Generally, the model/view classes can be separated into the three groups described above: models, views, and delegates. Each of these components is defined by abstract classes that provide common interfaces and, in some cases, default implementations of features. Abstract classes are meant to be subclassed in order to provide the full set of functionality expected by other components; this also allows specialized components to be written.
Models, views, and delegates communicate with each other using signals and slots:
- Signals from the model inform the view about changes to the data held by the data source.
- Signals from the view provide information about the user’s interaction with the items being displayed.
- Signals from the delegate are used during editing to tell the model and view about the state of the editor.
根据上面的介绍,模型/视图的类可以分为三类:模型、视图和代理,它们都有相应的抽象类提供通用的接口和某些功能的默认实现。抽象类就意味着要被其他类继承,根据需求提供对应的实现。
模型、视图和代理之间使用信号槽进行通信:
- 数据源中的数据发生变化时,模型发射信号通知视图
- 用户和视图交互时视图会发射信号,例如点击 view item,信号的参数包含了被交互的 view item 的信息
- 编辑数据项的时候代理会把编辑器的状态通过信号通知模型和视图
模型
All item models are based on the QAbstractItemModel class. This class defines an interface that is used by views and delegates to access data. The data itself does not have to be stored in the model; it can be held in a data structure or repository provided by a separate class, a file, a database, or some other application component.
The basic concepts surrounding models are presented in the section on Model Classes.
QAbstractItemModel provides an interface to data that is flexible enough to handle views that represent data in the form of tables, lists, and trees. However, when implementing new models for list and table-like data structures, the QAbstractListModel and QAbstractTableModel classes are better starting points because they provide appropriate default implementations of common functions. Each of these classes can be subclassed to provide models that support specialized kinds of lists and tables.
The process of subclassing models is discussed in the section on Creating New Models.
所有的 item 模型都是基于类 QAbstractItemModel 实现的。视图和代理使用 QAbstractItemModel 定义的接口访问数据。数据不一定是保存在模型中,也可以保存在其他类、文件、数据库或者其他应用中。
模型相关的概念在模型的类一节中进行介绍。
模型类 QAbstractItemModel 定义的访问数据接口 (函数) 是很灵活的,能够满足表格、列表和树用来显示模型的数据。然而,当给列表和表格自定义新的模型时,继承 QAbstractListModel 或者 QAbstractTableModel 是个很好的选择,因为他们提供了很多通用操作的默认实现,就不需要我们再重复实现。
实现自定义模型在创建新的模型类一节中进行介绍。
Qt provides some ready-made models that can be used to handle items of data:
- QStringListModel is used to store a simple list of QString items.
- QStandardItemModel manages more complex tree structures of items, each of which can contain arbitrary data.
- QFileSystemModel provides information about files and directories in the local filing system.
- QSqlQueryModel, QSqlTableModel, and QSqlRelationalTableModel are used to access databases using model/view conventions.
If these standard models do not meet your requirements, you can subclass QAbstractItemModel, QAbstractListModel, or QAbstractTableModel to create your own custom models.
Qt 已经提供了一些可用于处理数据项的模型:
- QStringListModel 用于存储简单的列表数据,数据项为 QString
- QStandardItemModel 用于管理有树结构关系的数据项,每个数据项可以包含任意的数据
- QFileSystemModel 访问本地文件系统的文件和文件夹
- QSqlQueryModel, QSqlTableModel 和 QSqlRelationalTableModel 使用模型视图的方式访问数据库
如果这些标准的模型还不能满足我们的需求,可以继承 QAbstractItemModel, QAbstractListModel, or QAbstractTableModel 实现自定义的模型类。
